Deploying Azure Functions using Blue-Green Deployment Model
Posted on
December 29, 2022
•
4 minutes
•
669 words

Table of contents
Introduction
In my previous blog post , I shared the steps that walk you through the basic concepts to deploy Azure Functions with GitLab CICD, and now it’s a good time to demonstrate the swap slot that helps you to plan for the simple blue-green deployment model.
What is Blue-Green deployment model?
A blue/green deployment is a strategy in which you create two separate but identical environments. One environment (blue) runs the current application version, and another (green) runs the new version. A blue/green deployment strategy increases application availability and reduces deployment risk by simplifying the rollback process if a deployment fails.
High Level
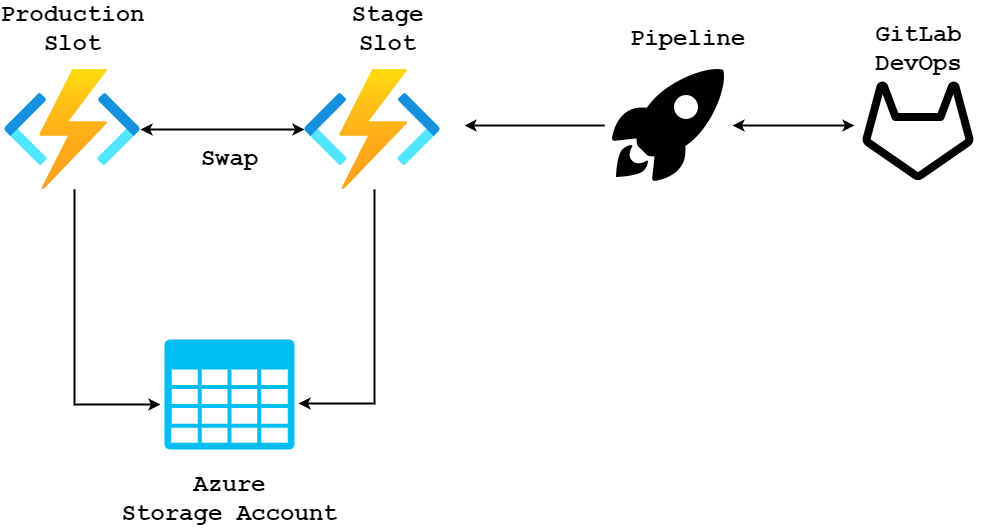
Solution
- We continue to use the same remote backend configuration, and also I removed the KICS scan stages. So in this pipeline, we do Terraform init, validate, plan and apply.
- The deployment (deploy) stage is to deploy the Azure Functions to the respective slot.
- Swap-Slot is to swap the function app slot from staging to production. When the value for the swap slot variable is Yes, the job enacts the swap.
Variables
variables:
Environment: qa
Function_App_Name: 'mikroapi'
TF_ADDRESS: "https://gitlab.com/api/v4/projects/${CI_PROJECT_ID}/terraform/state/${Environment}"
SLOT_NAME: 'staging'
SWAP_SLOT: 'yes'
- The
environmentstring is as per the naming convention of your choice. Function_App_Nameis name of your function app.TF_ADDRESSholds the HTTP address for the remote state management.SLOT_NAMEis the slot name. You can name as staging, QA or blue/green.
stages
stages:
- "validate"
- "plan"
- "apply"
- "deploy"
- "swap-slot"
- simple stages to do terraform
validate,planandapply. deployAzure Functions into the Function app.- Set the value for the
swap-slot.$swap-slot == yes, is to swap!
Before Script
.before_script_template:
before_script:
- $Credential = [pscredential]::new(${ARM_CLIENT_ID}, $(${ARM_CLIENT_SECRET} | ConvertTo-SecureString -AsPlainText -Force))
- Connect-AzAccount -TenantId "${ARM_TENANT_ID}" -Credential $Credential -ServicePrincipal
- cd terraform
- terraform init -backend-config=address="${TF_ADDRESS}" -backend-config=lock_address="${TF_ADDRESS}"/lock -backend-config=unlock_address="${TF_ADDRESS}"/lock -backend-config=username="${TF_USERNAME}" -backend-config=password="${TF_PASSWORD}" -backend-config=lock_method=POST -backend-config=unlock_method=DELETE -backend-config=retry_wait_min=5
- Connect to Azure tenant.
- Change the directory to Terraform, where the configuration files are stored.
- The terraform init command initializes a working directory containing configuration files and installs plugins for required providers.
Validate
validate:
stage: validate
extends: .before_script_template
tags:
- "cv-sandbox-1983"
only:
changes:
- "terraform/**/*"
script:
- terraform validate
validateruns checks that verify whether a configuration is syntactically valid and internally consistent, regardless of any provided variables or existing state. It is thus primarily useful for verifying reusable modules, including the correctness of attribute names and value types.
Plan
plan:
stage: plan
extends: .before_script_template
tags:
- "cv-sandbox-1983"
only:
changes:
- "terraform/**/*"
script:
- |
terraform plan `
-var="resource_group_name=rgp-${Function_App_Name}-${Environment}" `
-var="location=${location}" `
-var="storage_account_name=${Function_App_Name}stg${Environment}" `
-var="storage_account_tier=${storage_account_tier}" `
-var="storage_account_replication_type=${storage_account_replication_type}" `
-var="app_service_plan=${Function_App_Name}-${Environment}" `
-var="app_service_plan_tier=${Standard}" `
-var="app_service_plan_size=${app_service_plan_size}" `
-var="function_app_name=${Function_App_Name}-${Environment}" `
-var="function_app_slot_name=${SLOT_NAME}" `
-out "plan.cache"
artifacts:
paths:
- "terraform\\plan.cache"
dependencies:
- "validate"
- The
plancommand reports on infrastructure changes but does not apply any of the proposed changes. Instead, it creates a reviewable execution plan, which you can use to confirm that the proposed changes are as expected.
Apply
apply:
stage: apply
extends: .before_script_template
tags:
- "cv-sandbox-1983"
only:
changes:
- "terraform/**/*"
script:
- terraform apply -input=false plan.cache
dependencies:
- "plan"
- The
applycommand executes the actions proposed in a terraform plan
Deploy
deploy:
stage: deploy
tags:
- "cv-sandbox-1983"
only:
changes:
- "src/**/*"
script:
- az login --service-principal -u $ARM_CLIENT_ID -p $ARM_CLIENT_SECRET --tenant $ARM_TENANT_ID
- Start-Sleep -Seconds 150
- func azure functionapp publish "${Function_App_Name}-${Environment}" --powershell --prefix src/ --slot $SLOT_NAME --force
deploythe Azure Functions into the Function App. (Not on the default production slot)
Swap Slot
swap-slot:
stage: swap-slot
only:
variables:
- $SWAP_SLOT == "yes"
tags:
- "cv-sandbox-1983"
script:
- echo "ready to swap slot to production"
- az login --service-principal -u $ARM_CLIENT_ID -p $ARM_CLIENT_SECRET --tenant $ARM_TENANT_ID
- az functionapp deployment slot swap -g "rgp-${Function_App_Name}-${Environment}" -n "${Function_App_Name}-${Environment}" --slot "$SLOT_NAME" --target-slot "production"
swap-slotis to swap the slot from blue to green
Summary
Congratulations, you have successfully deployed the serverless solution with an additional slot. Now that you know the way to plan for the blue-green deployment. In my upcoming blog post, I have plans to cover the below
🚀 Implement a DevOps way to handle the enhancements.
🚀 Blue Green Deployment.